Exploring the realm of Sybau reveals an exciting landscape where innovative building materials and advanced construction techniques are shaping the future of architecture. With a focus on design principles that prioritize environmental harmony, architects and engineers are continually developing methods that seamlessly blend functionality with aesthetic appeal. This article offers an overview of emerging building trends and evolving technologies that contribute to more sustainable practices in the architectural field.
Key Takeaways
- Innovative materials like self-healing concrete and 3D-printed components revolutionize building durability and design flexibility.
- Smart technologies automate building management, optimizing energy, comfort, and environmental response.
- Green roofs and living walls enhance aesthetics, air quality, and ecological benefits in urban structures.
- Prefab and modular construction speed up timelines, improve quality, and support flexible architectural designs.
- Energy-efficient design uses natural light, ventilation, and insulation to reduce energy consumption sustainably.
Innovative Building Materials and Techniques
Innovative building materials are transforming the construction industry by offering new possibilities for durability, aesthetics, and functionality. High-performance composites, such as fiber-reinforced plastics, provide increased strength while reducing weight, making structures more versatile and easier to assemble. Additionally, self-healing concretes incorporate microcapsules of healing agents that repair cracks automatically, enhancing long-term integrity without ongoing maintenance.
Advanced techniques in construction focus on minimizing waste and optimizing resource use. For instance, 3D printing technologies enable rapid fabrication of complex components with minimal material wastage, allowing for customized designs that were previously difficult or costly to produce. Similarly, laser-guided processes improve precision and reduce execution time during various phases of the build, contributing to improved overall quality.
These innovations not only streamline construction workflows but also open the door for creative architectural expressions. As a result, professionals can explore novel forms and structural systems that align with contemporary design trends, all while employing materials and methods that push beyond traditional boundaries. Such developments demonstrate the ongoing evolution within the industry, emphasizing ingenuity and adaptability at every stage of project development.
Supplementary articles: Analyzing Chargers vs Texans Match: Key Player Stats and Insights
Smart Building Technologies and Automation
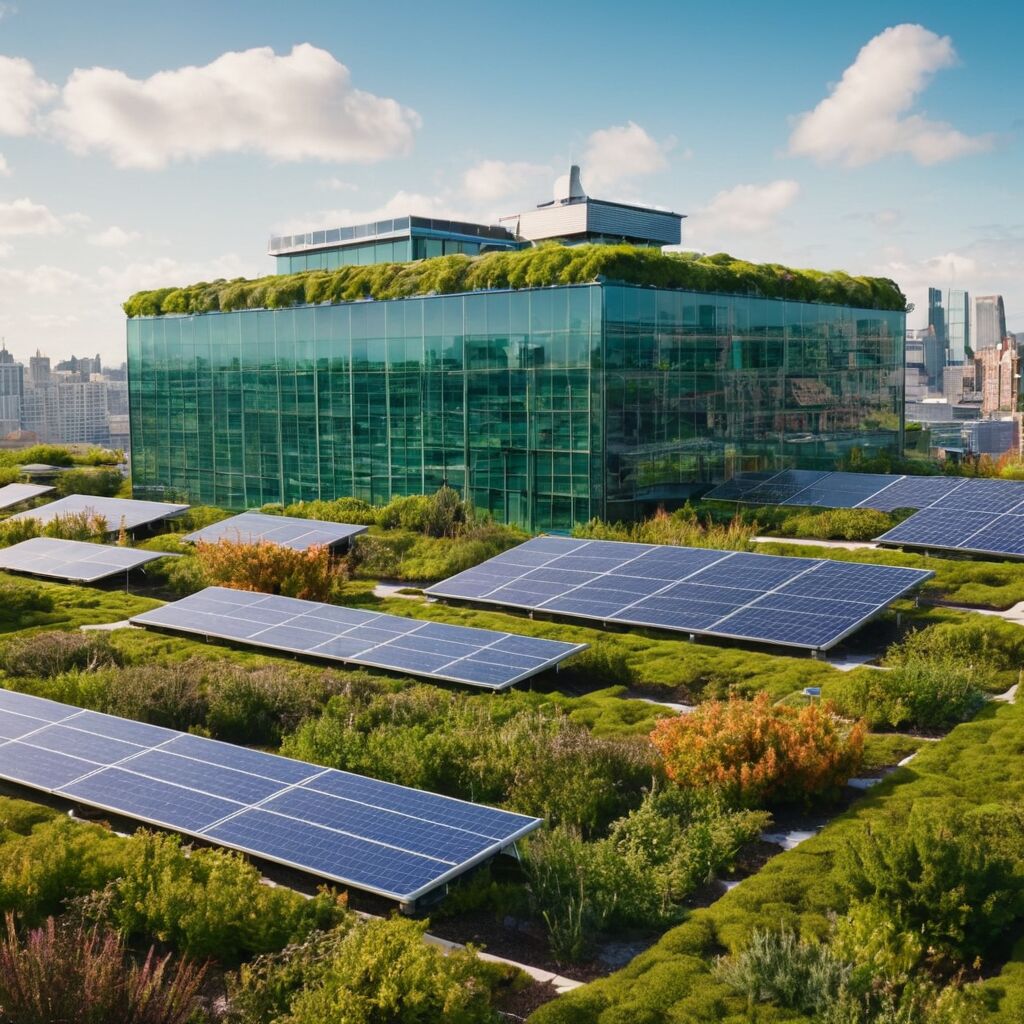

Smart building technologies are revolutionizing the way structures operate by integrating advanced automation systems that promote seamless interaction between various building components. These systems leverage sensors, data analytics, and interconnected devices to optimize functions such as lighting, heating, cooling, and security. The integration of intelligent control platforms allows for real-time adjustments that enhance occupant comfort and convenience without manual intervention.
One of the key benefits of these technologies is their ability to coordinate multiple systems through centralized management. By utilizing automated responses, buildings can adapt dynamically to changing conditions, such as adjusting indoor climate based on occupancy patterns or natural ventilation. This not only elevates user experience but also reduces unnecessary energy consumption, contributing to a more harmonious flow of resources inside the structure.
Furthermore, the adoption of machine learning algorithms enables systems to learn from historical data, improving their functionality over time. As a result, structures become more intuitive in anticipating occupant needs and responding proactively. The implementation of such technology fosters an environment where automation complements architectural design, creating spaces that are both functional and responsive to the daily rhythms of their inhabitants.
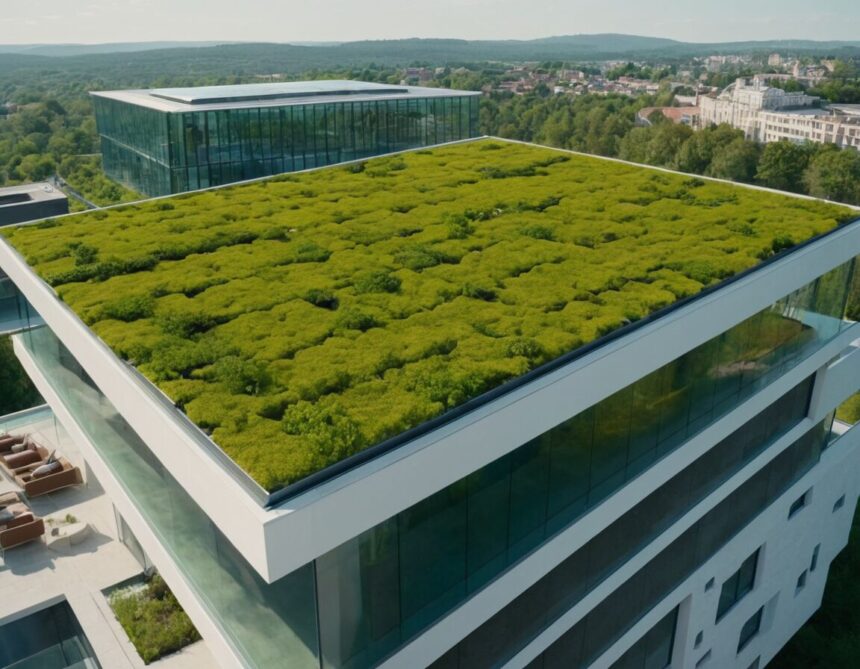
Green Roofs and Living Walls
Green roofs and living walls are innovative features that enhance building aesthetics while providing ecological benefits. These elements integrate vegetation directly into the structure, creating a natural layer that contributes to improved air quality and urban biodiversity. Green roofs consist of layered systems including a waterproof membrane, drainage components, and growing medium designed specifically for plant growth atop rooftops. They offer unique visual appeal and help mitigate heat island effects by reducing surface temperatures in dense urban environments.
On the other hand, living walls, also known as vertical gardens, involve planting vegetation on exterior or interior wall surfaces. This approach transforms blank facades into vibrant landscapes and fosters a connection between built spaces and nature. The incorporation of these green installations can assist with regulating indoor temperature by providing additional insulation, thereby contributing to more comfortable interiors without relying solely on mechanical systems.
Both techniques employ specialized irrigation and maintenance methods suited to their respective environments, ensuring healthy plant development over time. Their integration within architectural design not only enhances visual dynamics but also supports airflow and acoustic properties. As a result, green roofs and living walls serve as functional additions that blend form with environmental considerations, promoting adaptable and engaging built environments.
Architecture should speak of its time and place, but yearn for timelessness. – Frank Gehry
Prefab and Modular Construction Methods
Prefabricated and modular construction methods are transforming traditional building practices by offering a streamlined approach to assembling structures. Pre-assembled components are manufactured off-site in controlled environments, allowing for precise quality control and reduced on-site labor requirements. This process enables faster completion times, as modules or panels can be produced simultaneously with site preparations and then quickly assembled once delivered.
One of the key advantages of this approach is the ability to significantly reduce construction timelines. Since many elements are created concurrently in factories, project schedules become more predictable and less susceptible to weather-related delays. Additionally, these method’s flexibility allows for diverse designs, enabling architects and builders to adapt modules to various spatial configurations and aesthetic preferences with ease.
Another notable feature is the potential for improved accuracy in fabrication, which minimizes material wastage and enhances overall quality. Modular systems also facilitate easier upgrades and modifications over time, as individual units can be replaced or expanded without major structural interventions. Overall, prefabrication and modularization offer practical benefits that support innovative architectural forms while maintaining reliable construction processes.
More on this: The Impact of Funny Pictures on Social Media Engagement: Why Humor Matters
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Innovative Building Materials and Techniques | Transforming the construction industry with high-performance composites, self-healing concretes, 3D printing, and laser-guided processes that enhance durability, aesthetics, and resource efficiency. |
| Smart Building Technologies and Automation | Integrating sensors, data analytics, and intelligent control platforms to optimize energy use, improve occupant comfort, and enable buildings to respond proactively to environmental changes. |
| Green Roofs and Living Walls | Vegetation installations that enhance building aesthetics, air quality, and insulation, contributing to ecological benefits and urban biodiversity. |
| Prefab and Modular Construction Methods | Off-site manufacturing of building components that accelerate construction timelines, improve quality, and allow greater design flexibility and future upgrades. |
| Energy-Efficient Design Principles | Utilizing natural light, natural ventilation, and insulation strategies to reduce energy consumption and create sustainable, comfortable indoor environments. |
| Utilization of Local and Reclaimed Resources | Incorporating locally sourced and recycled materials to minimize environmental impact and promote sustainable resource use. |
| Integration of Natural Ventilation and Light | Design strategies that leverage natural airflow and daylight to enhance indoor air quality and reduce dependence on mechanical systems. |
| Community-Centric Architectural Approaches | Creating spaces that foster social interaction, inclusivity, and meet the needs of local communities, promoting sustainable urban development. |
Energy-Efficient Design Principles
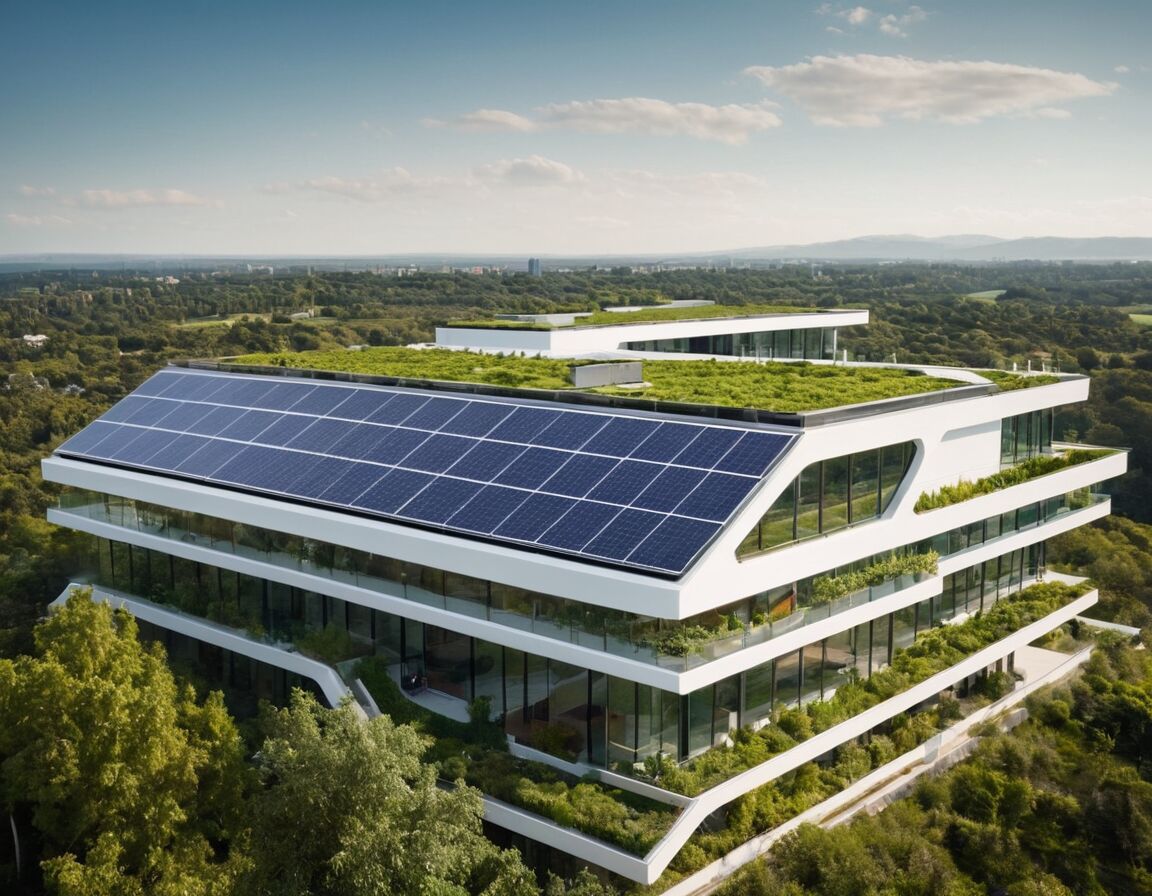

Energy-efficient design principles focus on creating structures that minimize energy consumption while maintaining comfort and functionality. One key aspect is maximizing the use of natural light through strategic placement of windows, skylights, and open spaces, which reduces dependence on artificial lighting during daytime hours. Additionally, integrating passive heating and cooling techniques, such as proper building orientation and shading devices, helps regulate indoor temperatures naturally.
Another important element involves enhancing insulation within walls, roofs, and floors to prevent unwanted heat transfer. When these components are well-insulated, interior temperatures remain stable, decreasing the workload on mechanical systems like heaters or air conditioners. Incorporating high-performance glazing can also aid in reducing heat loss or gain through windows, supporting overall energy moderation.
Furthermore, designing structures with natural ventilation pathways allows for airflow that cools interiors without the need for constant mechanical intervention. Combined with the strategic use of thermal mass materials that absorb and release heat gradually, these methods work together to create a balanced environment. Overall, thoughtful planning around material selection and spatial organization serves to optimize resource use, ultimately contributing to a more harmonious interaction between the built environment and its occupants.
Further reading material: The Mysterious World of Bill Cipher: Unraveling the Secrets of Gravity Falls’ Iconic Villain
Utilization of Local and Reclaimed Resources

The utilization of local and reclaimed resources plays a crucial role in modern architectural practices. By incorporating materials sourced directly from the surrounding environment, builders can reduce transportation distances, which in turn minimizes carbon emissions associated with material delivery. This approach also often leads to cost savings, as locally available resources tend to be more affordable and readily accessible.
Reclaimed materials, such as salvaged wood, bricks, and metal components, not only add unique aesthetic qualities to structures but also contribute to reducing waste. Repurposing existing materials prevents unnecessary landfill accumulation and preserves the embodied energy invested during their original manufacturing process. These elements can be integrated into various aspects of construction, including flooring, facades, and interior details, providing a distinctive character that reflects regional history and craftsmanship.
In addition, sourcing from nearby suppliers encourages support for local economies while fostering stronger community relationships. This practice may involve collaborating with regional artisans or craftsmen who specialize in repurposing materials, thereby promoting traditional techniques alongside contemporary design. Overall, the deliberate choice to utilize local and reclaimed resources enhances the connection between structure and its context while upholding a responsible approach towards material usage within the building sector.
Integration of Natural Ventilation and Light
Natural ventilation and daylight integration are fundamental elements in contemporary architectural design, promoting a harmonious relationship between indoor spaces and their environment. By carefully positioning windows, vents, and other openings, architects can harness prevailing breezes to facilitate airflow, reducing reliance on mechanical systems for cooling or air circulation. This approach not only enhances occupant comfort but also minimizes energy consumption associated with artificial climate control.
Strategic placement of openings ensures that fresh air can enter spaces while stale air exits, creating a natural cycle that maintains indoor air quality. Additionally, the use of operable windows and cross-ventilation pathways allows for adjustable airflow, adapting to changing weather conditions and user preferences. Properly designed layouts enable spaces to benefit from outdoor breezes without sacrificing privacy or security.
Incorporating natural light through well-designed window arrangements, skylights, and translucent materials increases visual comfort and reduces dependence on electrical lighting during daytime hours. Light-colored interior surfaces reflect illumination throughout rooms, amplifying brightness while decreasing energy needs. The thoughtful combination of these techniques results in ambiance that feels inviting, lively, and connected with the surrounding environment—creating internal zones that respond dynamically to external conditions and human activity.
Community-Centric Architectural Approaches
Community-centric architectural approaches focus on designing spaces that foster social interaction and promote a sense of belonging among residents. These designs prioritize creating environments where individuals feel connected to one another, encouraging collaboration and shared experiences. Such spaces often incorporate communal areas like parks, open courtyards, or multi-purpose rooms that serve as gathering points for diverse groups.
By integrating local cultural elements and respecting regional traditions, architects can enhance the relevance of these developments within their surroundings. This approach ensures that structures respond to the unique character of the area while supporting inclusive participation from community members during planning and development processes. Engaging residents early in project phases helps tailor solutions that genuinely reflect their aspirations and values.
Furthermore, design choices such as pedestrian-friendly pathways, accessible public amenities, and flexible layouts help facilitate everyday interactions and accommodate various activities. These features contribute to vibrant neighborhoods where social bonds are strengthened through shared use of space. Emphasizing transparency and openness throughout the design encourages trust and fosters relationships, nurturing a positive environment for all inhabitants.
FAQ: Your Questions Answered
How do sustainable architecture practices influence urban planning?
What are the economic benefits of adopting innovative building materials?
How do green roofs and living walls contribute to climate change mitigation?
What challenges are associated with modular construction in sustainable architecture?
How can natural ventilation be optimized in high-rise buildings?
References: